Prostate Cancer
—Specialisation
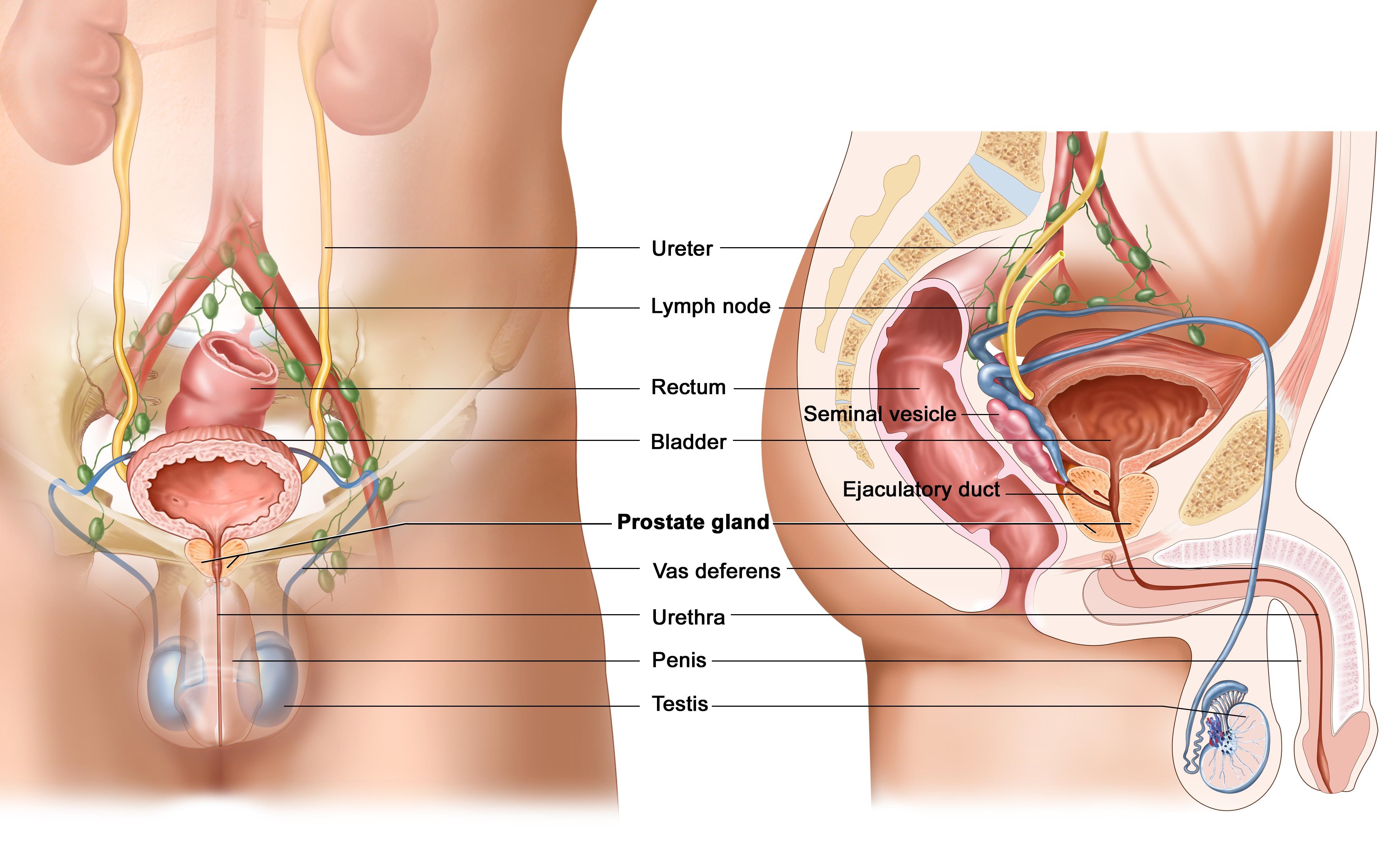
Signs & Symptoms
When the condition goes beyond the acceptable levels and go with the advanced levels, there will be additional following symptoms, like the following.
Diagnosis
Apart from the above two tests, there are also other tests done to confirm by gathering some more information relative to the urinary tract and prostate. It includes the test called DRE or Digital Rectal Examination that could reveal the abnormalities related to the prostate. Another test is the cystoscopy that could reveal the condition of the urinary tract, viewed from inside the bladder. Transrectal ultrasonography is another test that could provide a clear picture of the prostate, through the sound waves.
Prostate Imaging
Prostate imaging is done by either of the methods, like Magnetic Resonance Imaging or ultrasound.
Gleason Score
The tissue samples that are extracted from the diagnosis procedure called biopsy, are examined for the presence or absence of the cancer cells. The evaluation is done through Gleason score or microscopic features. The score reveals the presence and over-expressive protein called prostate specific membrane antigen.
Tumor Markers
Tumor markers is the test conducted to test the tissue samples to test the prensec of the tumor markers like PSA.
Staging
In addition to the finding of the cancerous cells in the prostate, the following important diagnosis to be done is the staging to understand and determine, what the criticality of the condition is. It can reveal how far and how wide the cancer cells have been spread. It is a key point to define the prognosis and help to select the necessary therapies to treat the condition. The stages will be TNM or Tumor/Nodes/Metastases. Other important aspects are size of the tumor, presence of the metastases, in addition and number of lymph nodes found.
Treatments Available
Early Stage
When the cancer is in the initial stages, the treatment recommended will be the following.
A-Watchful Waiting
B-Radical Prostatectomy
C-Conformal Radiotherapy
D-Brachytherapy
E-Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy
Advanced Stage
For advanced staged prostate cancer, advanced treatment options are available like hormone therapy, radiotherapy or sometimes in combination.
